If you’re searching for information about Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty, then this is the right blog for you. Berlin was a renowned political philosopher who made significant contributions to the field of liberalism. One of his most famous works is the essay titled “Two Concepts of Liberty,” where he introduces his ideas on positive and negative liberty.
In this article, we will explore Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty and their significance in today’s society. We will delve into his background, define positive and negative liberty, compare the two concepts, and examine their ongoing relevance. We will also discuss the critiques and controversies surrounding Berlin’s ideas.

Key Takeaways:
- Isaiah Berlin was a notable political philosopher who introduced the concepts of positive and negative liberty.
- Positive liberty is the freedom to pursue one’s goals and interests, while negative liberty is the absence of external constraints.
- The two concepts of liberty have important implications for individual rights and are still relevant in contemporary society.
- Critiques and controversies surround Berlin’s ideas, highlighting the ongoing debates in the field of political philosophy.
Understanding Isaiah Berlin’s Two Concepts of Liberty, Background, and Influence
Isaiah Berlin was a political philosopher and historian of ideas, known for his contributions to political theory and liberalism. He was born in Riga, Latvia, in 1909, into a wealthy Jewish family. The family moved to St. Petersburg when he was six years old, and then to London in 1921, where Berlin grew up.
Berlin was educated at St. Paul’s School, London, and went on to study classics at Oxford University. He later taught at Oxford, All Souls College, and subsequently at the University of London, where he was president of Wolfson College.
Berlin’s writings on political philosophy and the history of ideas were very influential. His most famous work, “Two Concepts of Liberty,” was published in 1958 and remains a classic of political philosophy. Throughout his career, Berlin was a strong advocate of liberalism, arguing for the importance of individual liberty and pluralism in society.
Notable Works by Isaiah Berlin
| Title | Year Published |
|---|---|
| Historical Inevitability | 1954 |
| Two Concepts of Liberty | 1958 |
| Four Essays on Liberty | 1969 |
| The Roots of Romanticism | 1999 |
Isaiah Berlin’s ideas on liberty continue to shape contemporary political discourse. His work on value pluralism, for example, has been cited as a justification for multiculturalism and the protection of diverse cultures. Furthermore, his advocacy for negative liberty as a means of protecting individual rights has influenced debates on issues such as privacy, free speech, and government surveillance.

Introducing Positive Liberty: Freedom to
Positive liberty refers to the concept of providing individuals with the necessary resources and opportunities to pursue their goals and fulfill their potential. According to Isaiah Berlin, positive liberty is the freedom to do something, particularly to achieve one’s goals and aspirations.
He argued that positive liberty should not be conflated with negative liberty, which is the absence of external constraints. Instead, positive liberty requires the active intervention of the state or society to ensure that individuals have the necessary resources and opportunities to achieve their goals.
A key characteristic of positive liberty is its focus on collective goals and the common good. In other words, individuals are not only free to pursue their own goals but also to contribute to the well-being of society as a whole. This involves the recognition that individual freedom is not absolute and must be balanced against the interests and needs of the community.
However, the achievement of positive liberty is not without controversy. Critics argue that it may lead to the imposition of the state’s idea of the good life on individuals and limit their individual freedom. They also argue that the state may not have the necessary knowledge or resources to effectively promote positive liberty.

“Liberty is liberty, not equality or fairness or justice or culture, or human happiness or a quiet conscience.” – Isaiah Berlin
Exploring Negative Liberty: Freedom from
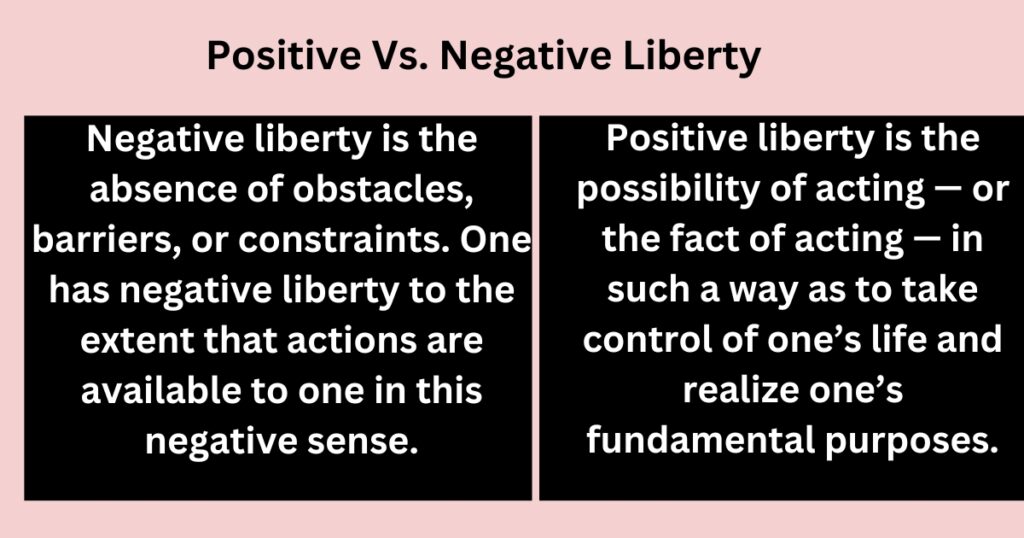
In contrast to positive liberty, negative liberty is freedom from external constraints. Isaiah Berlin believed that negative liberty was essential for individuals to pursue their own goals and make choices without interference from others. He famously stated that negative liberty meant “not being interfered with by others.”
According to Berlin, negative liberty can be achieved by limiting the power of the state and other institutions that may constrain individual freedom. This includes protecting individual rights and ensuring that laws do not impose unnecessary limitations on personal freedom.
One of the key distinctions between positive and negative liberty is that while positive liberty may require external resources and support, negative liberty does not. Negative liberty is primarily concerned with removing external barriers to individual freedom, rather than providing resources for individuals to pursue their goals.
For example, a person who is free from external constraints may choose to pursue a career in acting, even if their family or society pressures them to become a doctor. Negative liberty allows individuals to pursue their own goals without interference, even if others may not agree with their choices.
Isaiah Berlin argued that negative liberty is crucial for protecting individual rights and preserving democratic societies. Without negative liberty, individuals may be subject to arbitrary power and control, which can lead to oppression and tyranny.
As the image below illustrates, negative liberty is often associated with concepts such as individualism, liberalism, and laissez-faire economics.

“Liberty not only means that the individual has both the opportunity and the burden of choice; it also means that he must bear the consequences…Freedom and responsibility are inseparable.”
Overall, negative liberty is a crucial component of Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty. While positive liberty may be necessary for individuals to achieve their goals, negative liberty is essential for protecting individual rights and ensuring that individuals are free from external constraints. By understanding the importance of both concepts, we can better appreciate the complexity of individual freedom and the role that institutions play in preserving it.
Comparing Positive and Negative Liberty
Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty, positive and negative, are often contrasted with one another. Positive liberty concerns the freedom to pursue one’s personal goals and aspirations without external constraints. In contrast, negative liberty concerns the freedom from, such as the absence of external constraints that limit or prevent individuals from acting as they please.
Positive Liberty:
| Definition: | Freedom to pursue one’s personal goals and aspirations without external constraints. |
|---|---|
| Key Characteristics: | Associated with collective action and social justice, it requires state intervention or regulation, the pursuit of a common good. |
| How to Achieve: | By removing external constraints that prevent individuals from pursuing their goals, we create a society that fosters individual development and personal fulfillment. |
| Implications: | Requires a strong state to achieve, can be seen as authoritarian, and can lead to collective tyranny instead of individual freedom. |
Negative Liberty:
| Definition: | Freedom from external constraints that limit an individual’s ability to act as they please. |
|---|---|
| Key Characteristics: | Associated with individualism and personal autonomy, it requires limits on state intervention or regulation, the pursuit of individual rights and freedoms. |
| Importance: | Protects individuals from external coercion, promotes individual rights and freedoms, and allows for the pursuit of individual goals and aspirations. |
While positive and negative liberty are often contrasted, they are not necessarily mutually exclusive. Both concepts are important in promoting individual freedom and development. However, there are ongoing debates surrounding the implications of each concept and how best to achieve them in contemporary society.
The Significance of Isaiah Berlin’s Two Concepts of Liberty Today
Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty continue to be relevant and significant in contemporary society. The concepts of positive and negative liberty reflect our understanding of freedom and individual rights and have implications for various political and social issues.
Positive liberty, which refers to the freedom to achieve one’s goals and potential, is often linked to the concept of social justice. It implies that the state has a responsibility to provide individuals with the resources and opportunities necessary to achieve their goals. This idea is reflected in debates surrounding issues such as access to education and healthcare.
Negative liberty, on the other hand, is focused on protecting individuals from external constraints and interference. It emphasizes the importance of limiting the power of the state and preserving individual autonomy. This concept is relevant in debates surrounding issues such as privacy and civil liberties.
Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty also continue to shape debates and discussions surrounding multiculturalism and diversity. The concept of positive liberty has been invoked to argue for the importance of promoting cultural diversity and recognizing the experiences of marginalized groups. The concept of negative liberty has been used to critique policies or practices that limit individual expression or freedom in the name of cultural sensitivity.
The ongoing debates around these two concepts also highlight the complexity and challenges of achieving a balance between positive and negative liberty. While positive liberty can potentially enhance individual freedom, it also requires the state to intervene in people’s lives and potentially limit their autonomy. Negative liberty, on the other hand, may prioritize individual autonomy but may also lead to social and economic inequality.
Overall, the enduring significance of Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty lies in their ability to provide a framework for thinking about complex political and social issues. By understanding the nuances and implications of these concepts, we can better navigate debates around individual rights, social justice, and diversity in contemporary society.
Critiques and Controversies Surrounding Berlin’s Concepts
While Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty have gained widespread recognition, they have also faced criticism and controversy. Some scholars argue that Berlin’s emphasis on negative liberty undermines the importance of positive liberty and the government’s role in promoting it. Others have criticized Berlin’s individualistic approach, which overlooks the importance of collective action and social justice in achieving liberty.
Moreover, some have argued that Berlin’s definitions of positive and negative liberty are too vague and open to interpretation. According to these critics, the concepts fail to provide a clear roadmap for achieving freedom and may even lead to contradictory outcomes.
For example, critics have pointed out that the emphasis on negative liberty can lead to a laissez-faire approach to government, where the state does little to ensure equal opportunities and social welfare. Similarly, the focus on positive liberty can lead to authoritarianism, where the government assumes the role of dictating what is in the best interest of citizens.
Additionally, some critics have taken issue with Berlin’s binary classification of liberty, arguing that there may be other dimensions or forms of freedom that are not captured by his concepts.
Despite these critiques and controversies, Berlin’s two concepts of liberty remain influential in political philosophy and continue to shape our understanding of individual freedom and the role of the state in promoting it.
Conclusion
Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty, positive and negative liberty, continue to be relevant in today’s society as they shape our understanding of freedom and individual rights.
By exploring Berlin’s background and influence, we can see the significance of his ideas in the field of political philosophy. Positive liberty, which emphasizes the freedom to pursue one’s goals, and negative liberty, which emphasizes protection from external constraints, offer different perspectives on the meaning and purpose of liberty.
A comparison of the two concepts has highlighted their differences in terms of their definitions, goals, and implications. The ongoing debates and controversies that surround Berlin’s ideas demonstrate their significance and impact on contemporary political and social issues.
The Importance of Engaging with Berlin’s Ideas
Understanding and engaging with Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty is crucial to our understanding of freedom and individual rights. These ideas are essential to shaping our political and social systems, and promoting the values of democracy and human rights.
By critically examining and evaluating these concepts, we can better understand how they shape our society and identify areas where they may need to be reevaluated or reinterpreted to better reflect our changing world.
Overall, Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty offer valuable insights into the meaning and purpose of freedom in society. It is essential that we continue to engage with these concepts to promote the values of democracy, freedom, and individual rights.
FAQ
Q: What is the main topic of this article?
A: The main topic of this article is Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty.
Q: Who is Isaiah Berlin and why are his ideas on liberty significant?
Isaiah Berlin was a political philosopher known for his contributions to the understanding of liberty. His ideas on liberty are significant because they provide valuable insights into different perspectives on freedom and individual rights.
Q: What is discussed in Section 2?
A: Section 2 delves into Isaiah Berlin’s background and discuss his influence as a political philosopher. It will explore his education, career, and notable works to establish his authority on the subject of liberty.
Q: What is positive liberty?
A: Positive liberty refers to the freedom to pursue one’s own goals and desires, often through the development of one’s capacities and the elimination of external constraints.
Q: How can positive liberty be achieved, and what are its implications for society?
A: Positive liberty can be achieved through the creation of conditions that enable individuals to exercise their freedom effectively. Its implications for society include the recognition of social and economic rights, as well as the responsibility of the state to provide opportunities for self-realization.
Q: What is negative liberty?
A: Negative liberty refers to the absence of external constraints or interference, allowing individuals to act and make choices without interference from others.
Q: Why is negative liberty important?
A: Negative liberty is important as it protects individuals from external coercion and allows for personal autonomy and self-determination.
Q: What are the differences between positive and negative liberty?
A: Positive liberty focuses on the freedom to pursue one’s goals and the development of one’s capacities, while negative liberty emphasizes freedom from external constraints. They have different definitions, goals, and implications.
Q: How are Isaiah Berlin’s concepts of liberty relevant in today’s society?
A: Isaiah Berlin’s concepts of liberty continue to be relevant in today’s society as they help shape our understanding of freedom, individual rights, and the role of the state in promoting and protecting these rights.
Q: Are there any critiques and controversies surrounding Isaiah Berlin’s concepts?
A: Yes, there are critiques and controversies surrounding Isaiah Berlin’s concepts of liberty. Different perspectives and arguments have been presented, leading to ongoing debates in the field of political philosophy.
Q: What is discussed in the conclusion?
A: The conclusion summarizes the key points discussed in the article and provide a concluding statement on the significance of Isaiah Berlin’s two concepts of liberty. It will emphasize the importance of understanding and engaging with these concepts to inform our understanding of freedom and individual rights.
People Also Read: Liberty Is a Key Concept of in Political Science: A Powerful Guide










