In a diverse and populous country like India, effective governance requires a system that Panchayat Raj System brings decision-making closer to the grassroots level. The Panchayat Raj system, introduced as a constitutional amendment in 1992, aims to achieve this objective. This decentralized form of local governance has played a vital role in empowering communities, promoting participatory democracy, and fostering sustainable development. In this blog, we will delve into the Panchayat Raj system in India, exploring its significance, structure, functions, and impact.
Understanding the Panchayat Raj System
The term “Panchayat Raj” translates to “rule by the village council” and encompasses a three-tier system of local self-governance. At the base level, we have the Gram Panchayat, which represents a group of villages or a small town. Above it lies the intermediate level known as the Panchayat Samiti or Block Panchayat, which comprises a cluster of Gram Panchayats. Finally, at the apex, we have the Zilla Parishad or District Panchayat, which oversees multiple Panchayat Samitis within a district.
Significance of the Panchayat Raj System:
1. Grassroots Democracy: The Panchayat Raj system provides a platform for citizens to actively participate in decision-making processes at the local level. It fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment among community members, enabling them to voice their concerns, influence policies, and hold their elected representatives accountable.
2. Local Development: By devolving powers and resources to the grassroots level, the Panchayat Raj system ensures that development initiatives are tailored to the specific needs and priorities of the local population. It enables communities to address issues such as infrastructure development, healthcare, education, agriculture, and rural livelihoods in a more targeted and efficient manner.
3. Social Inclusion: Panchayats serve as an inclusive space where marginalized sections of society, such as women, Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and other backward classes, can actively participate in decision-making. This system helps address historical disparities and empowers these communities to contribute to development.
Functions of the Panchayat Raj System:
The Panchayat Raj institutions perform various functions, including:
1. Governance and Administration: Panchayats play a crucial role in maintaining law and order, issuing licenses and certificates, managing local resources, and ensuring the efficient delivery of public services.
2. Planning and Development: Panchayats are responsible for preparing and implementing local development plans, allocating funds, and executing projects aimed at improving the socio-economic conditions of their respective regions.
3. Social Welfare: Panchayats facilitate the implementation of social welfare schemes, including poverty alleviation programs, healthcare initiatives, education projects, and women empowerment programs.

Impact of the Panchayat Raj System:
The Panchayat Raj system has had a transformative impact on Indian society and governance:
1. Increased Participation: The system has empowered citizens, especially women and marginalized communities, by enabling their active involvement in decision-making processes. This has led to a more inclusive and representative democracy at the grassroots level.
2. Rural Development: Panchayats have played a vital role in bringing about positive changes in rural areas. They have facilitated the construction of infrastructure, improved access to basic amenities, and boosted local economies through sustainable agricultural practices and rural entrepreneurship.
3. Social Equity: Panchayats have been instrumental in addressing social inequalities by ensuring better representation and welfare measures for marginalized communities. They have contributed to reducing caste-based discrimination, promoting gender equality, and uplifting underprivileged sections of society.
Panchayat Raj and Reservation
The Panchayat Raj system in India has had a significant impact on the reservation policy in the country.
Reservation refers to the policy of reserving a certain percentage of seats or positions for historically disadvantaged communities or groups to ensure their representation and participation in various spheres of governance.
The 73rd Amendment Act of the Indian Constitution in 1992 introduced the Panchayati Raj system, which aimed to decentralize power and promote local self-governance. This amendment mandated reserving seats for Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and women in Panchayat Raj institutions at all levels—village, intermediate, and district 33 percent.
The impact of the Panchayat Raj system on reservations in India can be understood in the following ways:
1. Increased representation: The Panchayat Raj system has provided a platform for marginalized communities such as SCs, STs, and women to actively participate in decision-making. Reserving seats for these groups has increased their representation in local governance bodies.
2. Empowerment of marginalized communities: Reservation in Panchayat Raj institutions has played a crucial role in empowering marginalized communities. It has provided opportunities for these communities to hold leadership positions, voice their concerns, and influence local development policies and programs.
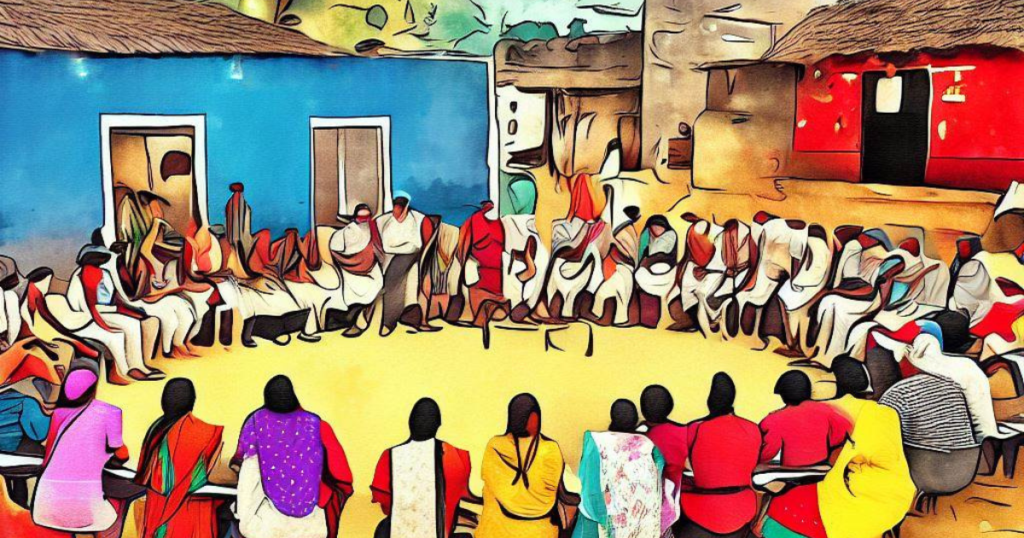

3. Social inclusion and participation: Reservation in Panchayat Raj institutions has helped in promoting social inclusion by ensuring the representation of marginalized communities. It has provided a platform for their voices to be heard and their perspectives to be considered in local decision-making processes.
4. Addressing historical injustices: The reservation policy in Panchayat Raj institutions aims to address historical injustices faced by marginalized communities. By providing reserved seats, it attempts to rectify the historical disadvantages and discrimination these communities have endured.
5. Strengthening democracy: The Panchayat Raj system, with its reservation policy, has contributed to strengthening democracy at the grassroots level. It has provided opportunities for broader participation, diversified leadership, and more inclusive governance, leading to a more representative democracy.
It is important to note that while the Panchayat Raj system and reservation policy have brought about positive changes, challenges remain in ensuring effective implementation, adequate representation, and empowering marginalized communities. Continued efforts are required to address these challenges and create a more inclusive and participatory local governance system in India.
Challenges and the Way Forward:
While the Panchayat Raj system has made significant strides, several challenges remain. These include inadequate financial resources, limited administrative capacity, political interference, and unequal representation. To further strengthen this system, efforts must be made to enhance transparency, improve fiscal autonomy, build capacity at the grassroots level, and ensure effective coordination between various tiers of governance.
Conclusion
The Panchayat Raj system in India has emerged as a powerful tool for decentralization, local governance, and community empowerment. By fostering grassroots democracy, promoting social inclusion, and driving sustainable development, this system has transformed the lives of millions. As India continues its journey towards progress, nurturing and strengthening the Panchayat Raj institutions will play a pivotal role in achieving inclusive and sustainable development across the nation.
- You Can Read:











1 thought on “Panchayat Raj System in India.”